Cervical cancer and human papillomavirus
Cervical cancer (CC) is characterized by a very high mortality rate. Every third woman suffering from cancer dies from cervical cancer. In part, such sad numbers are due to the difficulty of diagnosis and the woman’s insufficient attention to her health.
The risk of developing a tumor increases dramatically after 30 years. Usually, the development of a tumor takes 10-20 years with a long stage of precancer without any symptoms, however, there are aggressive forms that last 1-2 years. It is extremely difficult to cure developed cancer, and in the later stages it is often impossible. Therefore, every woman needs early diagnosis and timely prevention of cervical cancer.
The main cause of cervical cancer is the HPV virus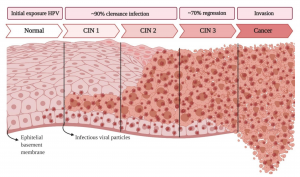
It has been proven that the main cause of cervical cancer is infection with the human papillomavirus (HPV). This virus is widespread, sexually transmitted and infects the lining of the cervix. Carriage of the virus in the early stages of infection does not manifest itself in any way.
Any woman who is sexually active is at risk of becoming a carrier of HPV.
In most cases, after infection, HPV is eliminated within a few months, but in some cases the infection can become chronic. It depends on the state of the host’s immunity, which is 30% due to hereditary factors (genetics) and the characteristics of the virus itself.
Variety of HPV
There are more than 100 different types of HPV, which are grouped into 2 main groups according to the degree of cancer risk (high and low). In Russia, the greatest danger is represented by the 16th and 18th types of HPV from the group of high cancer risk (for which the prophylactic vaccine Gardasil has already been created). It is also worth keeping in mind that simultaneous infection with several types of HPV is possible.
How does HPV cause cervical cancer?
Under certain conditions, the high-risk papilloma virus, after penetrating into the cervical cell, is able to integrate into DNA (integrate). Then the virus begins to produce oncoproteins E6 / E7, which disrupt the work of anticancer proteins, and the cells of the cervix begin to divide uncontrollably. As a result of this process, a tumor is formed.
How to determine the risk of developing cervical cancer?
As you know, the disease is easier to prevent than to cure, especially cancer.
Thanks to modern research methods in the MedLab laboratory, there is the possibility of early detection of patients infected with HPV. The method of polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and real-time PCR is used to determine the types of virus, quantity, integration, as well as to determine the risk of developing cervical cancer due to hereditary factors (genetics).
For the analysis of HPV carriage, a urogenital scraping is taken absolutely painlessly. If a woman is sexually active, HPV tests should be done to determine the type of the virus at least annually. The optimal set of analyzes for HPV is assembled into a complex for DNA typing of HPV with viral load and E6 / E7 oncoproteins (RT-PCR complex). You can also test for fewer variants of virus types HPV DNA typing (16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 45, 51, 52, 56, 58, 59 types) with an individual viral load (RT-PCR)
For gene diagnostics, blood is taken from a vein for the genetic profile of GP9. Cervical cancer – 5 predisposition genes. The test is carried out once and its results are relevant for life. If the level of individual risk of cervical cancer development turned out to be high, the patient will be assigned to the risk group, and forewarned means armed!
The virus was found. What’s next?
If HPV https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Human_papillomavirus_infection types of high cancer risk are detected, it is recommended to re-determine its type, amount (viral load) and integration.
If the viral load is low, monitoring is required, i.e. repeated tests at least once every six months.
At high viral loads, the doctor may prescribe immunomodulating and other drugs to eliminate the virus. Monitoring is required after treatment.
HPV can be cured like a common cold and cancer can be prevented – the main thing to know!