Polyp of the body of the uterus (endometrial polyp)
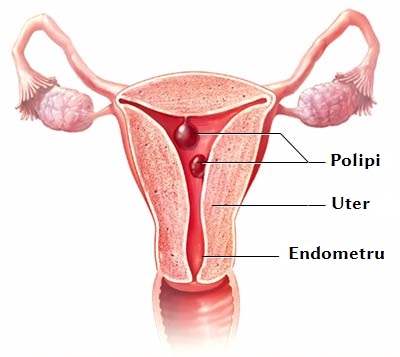
An endometrial polyp is a benign mass originating from the epithelium of the uterus (endometrium) and located in the uterine cavity.
Polyps are
glandular (more often in young women under 40)
glandular fibrous (can occur at any age)
fibrous (more often in women after 50 years)
adenomatous (precancerous)
Polyps are caused by:
hormonal disorders (thyroid pathology, polycystic ovary disease, obesity)
inflammatory diseases of the genital organs (including chronic cervicitis, vaginal dysbiosis, genital infections)
termination of pregnancy, miscarriages, history of abortion.
Manifestations of polyps
In most cases, polyps are asymptomatic and are accidentally detected during a routine examination. However, they may be accompanied by a violation of the menstrual cycle in the form of profuse menstruation, smearing spotting outside the cycle, as well as aching pains in the lower abdomen, profuse leucorrhoea.
Diagnostics
During a gynecological examination on a chair, it is impossible to diagnose a polyp of the uterus. For this, an ultrasound examination with a vaginal probe is used, which is preferably carried out immediately after the end of menstruation.
Treatment of uterine polyps
Detection of a polyp https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Polyp_(medicine) is an indication for its removal. For this, Hysteroscopy is used, which allows you to make an accurate diagnosis and immediately remove the polyp. Removal is performed using a laser or electrical energy with a special electrode. This is necessary so that there is no recurrence (re-emergence) of the polyp. When endometrial polyposis (multiple polyps) is detected, the uterine cavity is scraped out. The removed polyps are sent for a mandatory histological examination.
The operation takes place quickly, under intravenous anesthesia on an outpatient basis. After a short stay in the ward, the patient can be allowed to go home. There may be slight spotting for several days after the operation. In some cases, antibiotics are prescribed after surgery. After receiving the results of histology, the doctor prescribes the treatment necessary for recovery and prevention of relapse.